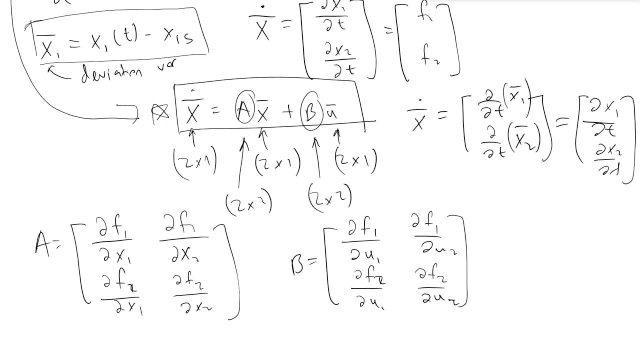Type
Experience
Scope
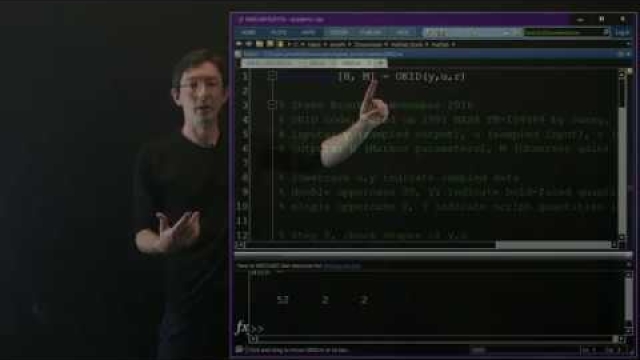
Data-Driven Control: ERA/OKID Example in Matlab
In this lecture, we explore the observer Kalman filter identification (OKID) and eigensystem realization algorithm (ERA) in Matlab on an example.
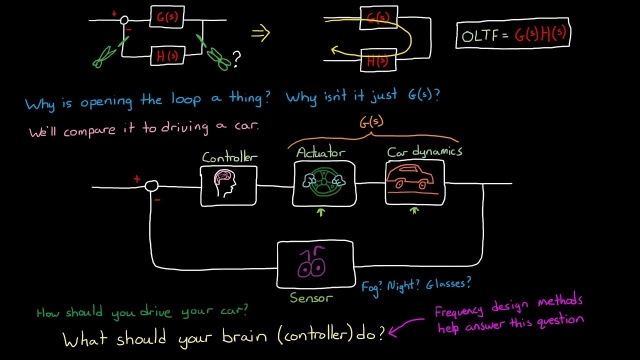
See MoreStandard HW Problem #2: Which is the real open loop transfer function?
In this video, we’ll go through another standard homework problem so you can see how you can apply many of the things you’re learning into a single problem. The question is, we have two...
See MoreSVD: Optimal Truncation [Python]
This video describes how to optimally truncate the singular value decomposition (SVD) for noisy data (Python code).
See MoreIntroduction to Bode Plots
In this video we introduce the concept of Bode plots including what they represent, how they are generated, as well as how to use Matlab tools to work with B...
See MoreDiscrete-Time Dynamical Systems
This video shows how discrete-time dynamical systems may be induced from continuous-time systems.
See MoreControl Systems Lectures - LTI Systems
This lecture describes what it means when we say a system is linear and time invariant. I also try to give an example as to why these systems are so important when designing control systems...
See MoreDerivation and Solution of Laplace’s Equation
In this video we show how the heat equation can be simplified to obtain Laplace’s equation. We investigate how to solve Laplace’s equation using separation ...
See MoreMachine Learning Overview
This lecture provides an overview of machine learning, and how it fits into this introductory video sequence on data science. We discuss how machine learning involves "modeling with data".
See MoreLaplace domain – tutorial 5: Inverse Laplace transform
In this video, we cover inverse Laplace transform which enables us to travel back from Laplace to the time domain. We will learn how to use simple tricks alo...
See MoreApollo's Flight Computer: Epitome of Engineering
The Apollo missions' success can be vastly accredited to the success of building a robust, one-of-a-kind flight computer for its guidance, navigation and control. Follow this video to...
See MoreA Nonlinear, 6 DOF Dynamic Model of an Aircraft: the Research Civil Aircraft...
In this video we develop a dynamic model of an aircraft by describing forces and moments generated by aerodynamic, propulsion, and gravity that act on the aircraft. This video outlines the...
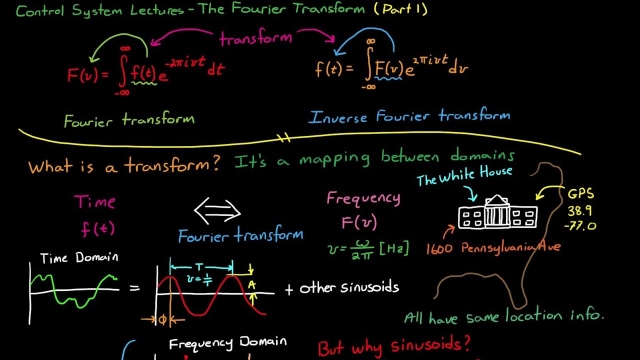
See MoreIntroduction to the Fourier Transform (Part 1)
This video is an introduction to the Fourier Transform. I try to give a little bit of background into what the transform does and then I go step by step through explaining the Inverse...
See MoreNeural Networks and Deep Learning
This lecture explores the recent explosion of interest in neural networks and deep learning in the context of 1) vast and increasing data sets, and 2) rapidly improving computational...
See MoreFrequency domain – tutorial 3: filtering (periodic signals)
In this video, we learn about filtering which enables us to manipulate the frequency content of a signal. A common filtering application is to preserve desi...
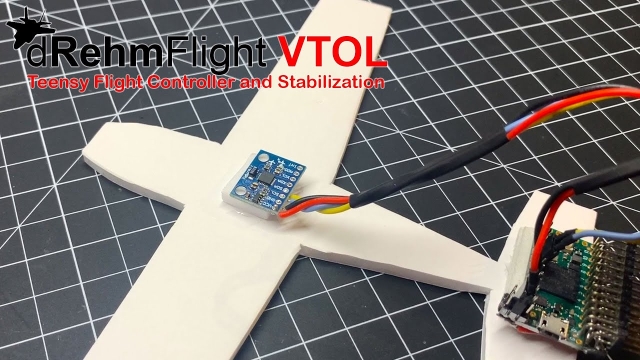
See MoreMounting and Configuring the IMU - dRehmFlight VTOL
This video will show you how to verify proper operation of the IMU for dRehmFlight VTOL before your first flight. It will also show you how to correctly mount the IMU to your aircraft. The...
See MoreLecture 11: Transient Response and Numerical Problems
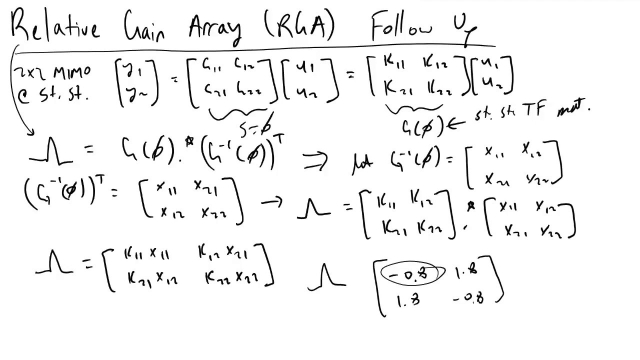
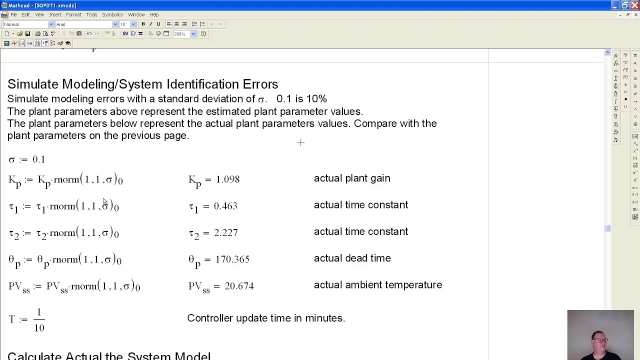
Relative Gain Array RGA Analysis
I cover how you can find the relative gain array from the steady state gain array, and interpret the results to determine which input to pair with which outp...
See MorePeter Ponders PID. Second Order Plus Dead Time , SOPDT, Temperature Control,...
In this video I derive the equations for the controller gains and a low pass filter for a SOPDT system with a very long dead time To make the simulation mo...
See MoreStandard HW Problem #1: PID and Root Locus
A walk through of a typical homework problem using the root locus method to tune a PID controller. This is the first in what may be a series of homework style problems I'll cover. This is...
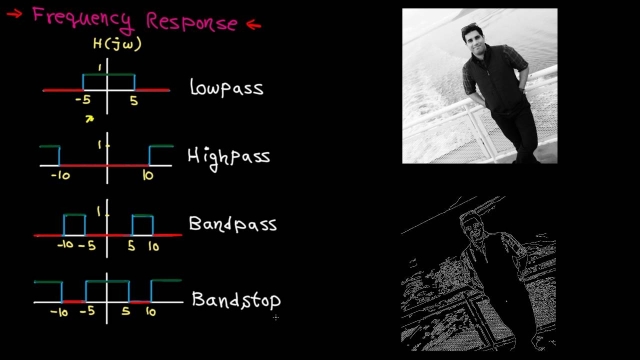
See MoreLecture 21: Introduction to Frequency Response
State Space in Process Control
An overview on how we can derive a state space model from a given set of state variables and inputs, as well as an intro to deviation variables. This is part...
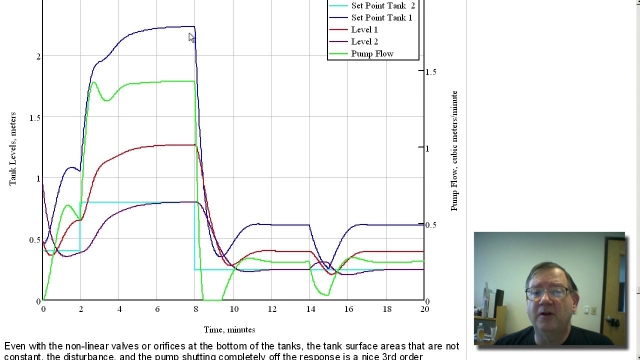
See MorePeter Ponders PID - Tank Level Control
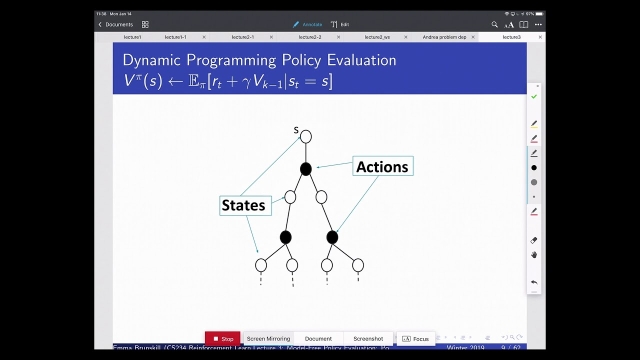
Stanford CS234: Reinforcement Learning | Winter 2019 | Lecture 3 - Model-Fr...
Professor Emma Brunskill
Assistant Professor, Computer Science
Stanford AI for Human Impact Lab
Stanford Artificial Intelligence Lab
Statistical Machine Learning Group
Lecture 23: Bode plots
Controls Engineering in the FIRST Robotics Competition
This guide is intended to make an advanced engineering topic approachable so it can be applied by those who aren’t experts in control theory. The intended audience is high school students...
See More
![SVD: Optimal Truncation [Python]](/sites/default/files/styles/search_resulkts/public/2020-12/maxresdefault_424.jpg?itok=UV9sowPB)