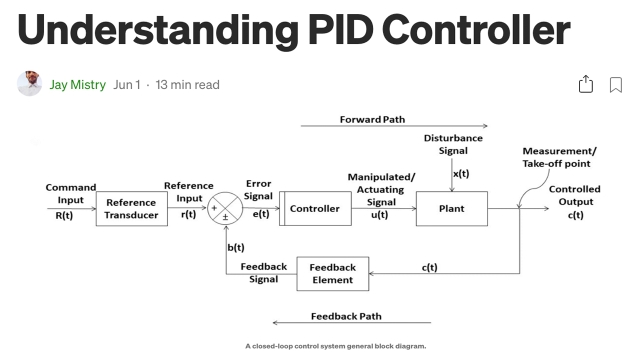
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value, e(t), as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms (denoted P, I, and D respectively), hence the name.
Topic
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Controller
This topic includes the following resources and journeys:
Type
Experience
Scope
Understanding PID Controller
This blog post begins by walking through the basics and the theoretical part of the PID controllers. The controller is then tested, verified, and analyzed using MATLAB.
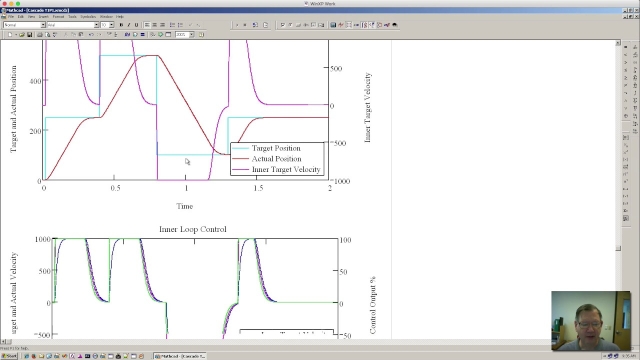
See MorePeter Ponders PID - Cascade Control Part2
The inner loop pole locations and gains are calculated first so the inner loop pole locations are determined by the user. The outer loop poles are still pla...
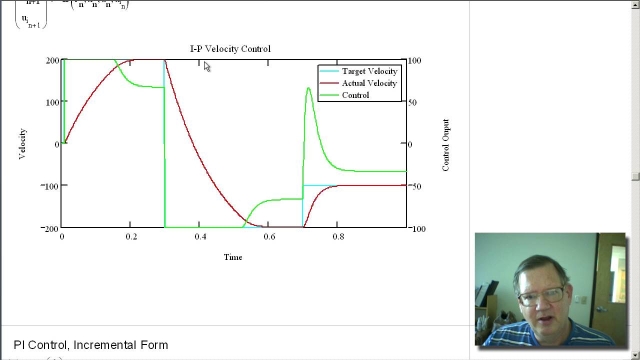
See MorePeter Ponders PID - Controlling a non-integrating single pole system. Part 3...
Part 3 uses PI control which is the only practical means of control a non-integrating single pole system.http://deltamotion.comhttp://forum.deltamotion.com
See MoreControl Bootcamp: Cruise Control Example with Proportional-Integral (PI) co...
In this video, we show that introducing integral control reduces the steady-state tracking error to zero in the cruise control example. We also use a more sophisticated model for the...
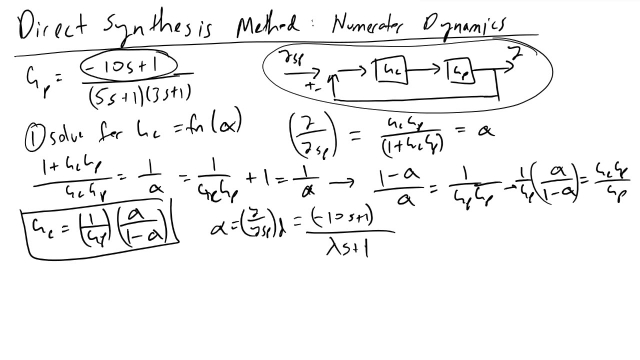
See MoreDirect Synthesis Method Numerator Dynamics Problem
I walk through how to design a PID feedback controller when given a second order process with numerator dynamics, using the Direct Synthesis Method.
See MoreUnderstanding PID Control, Part 2: Expanding Beyond a Simple Integral
The first video in this series described a PID controller, and it showed how each of the three branches help control your system.That seemed simple enough and appeared to work. However, in...
See More