A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value, e(t), as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms (denoted P, I, and D respectively), hence the name.
Topic
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Controller
This topic includes the following resources and journeys:
Type
Experience
Scope
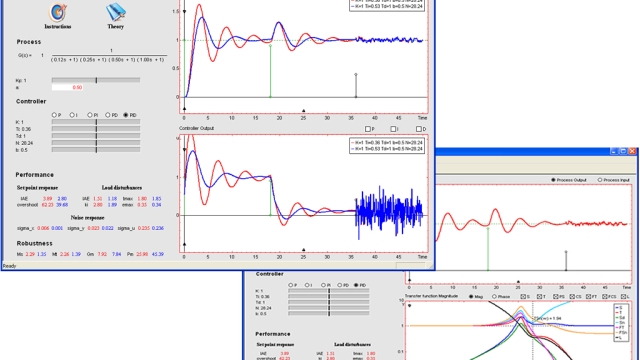
Interactive Tool for PID understanding
The module PID Basics is designed to explore the properties of a simple feedback loop by showing the time and frequency responses of a closed-loop system and demonstrating how these...
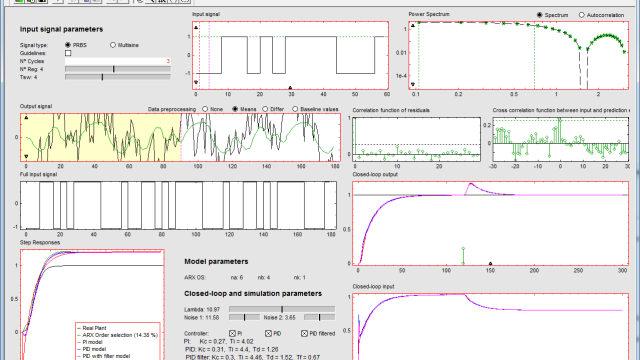
See Morei-pIDtune: An interactive tool for integrated system identification and PID ...
i-pIDtune is an interactive software tool that integrates system identification and PID controller design. The tool supports experimental design and execution under plant-friendly conditions...
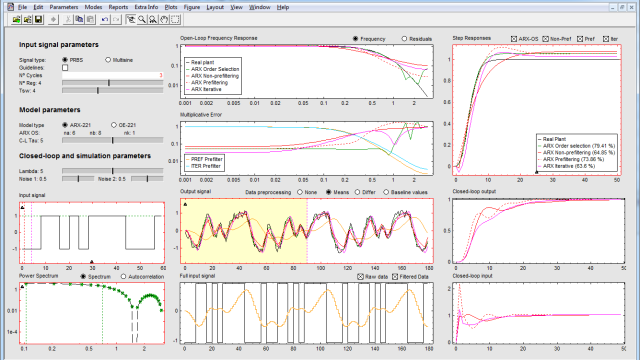
See MoreITCRI: An Interactive Software Tool for Control-Relevant Identification
The Interactive Tool for Control Relevant Identification (ITCRI) comprehensively captures the control-relevant identification process, from input design to closed-loop control, depicting...
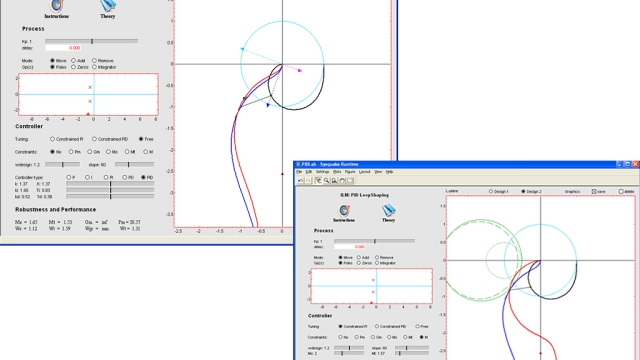
See MoreInteractive Tool for Loop Shaping understanding based on PID control
Loop shaping is a design method where it is attempted to choose a controller such that the loop transfer function obtains the desired shape. In this module the loop transfer function is...
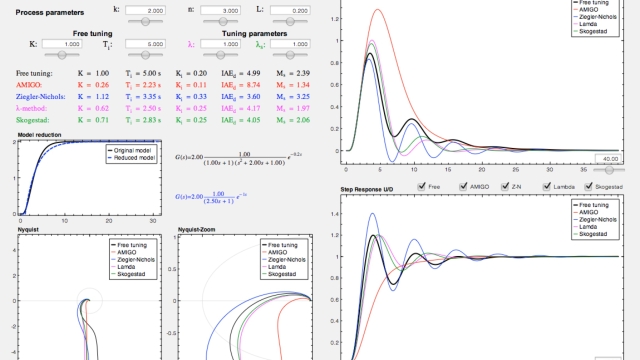
See MoreInteractive Tool about PID tuning rules
Hundreds of PID design methods are available in literature. Many of them are very similar and sometimes it is not straightforward to understand their purposes. This interactive software tool...
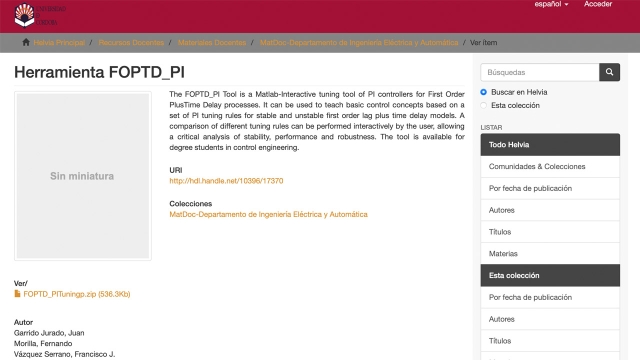
See MoreFirst Order Plus Dead Time Tuning App for PI Controllers
The FOPTD_PI Tool is a Matlab-Interactive tuning tool of PI controllers for First Order PlusTime Delay processes. It can be used to teach basic control concepts based on a set of PI tuning...
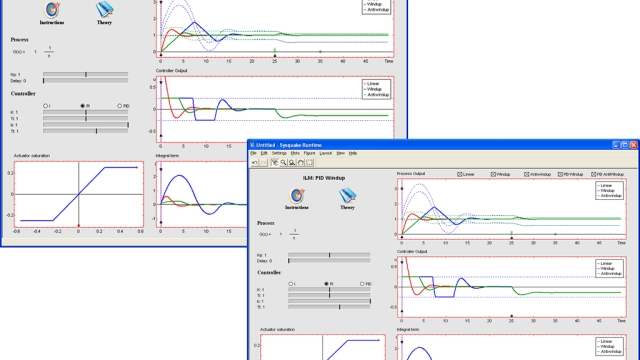
See MoreInteractive Tool about control signal saturation (windup) with PID control
The purpose of this module is to give a familiarity with the phenomenon of integral windup and a method for avoiding it. The module shows process outputs and control signals for unlimited...
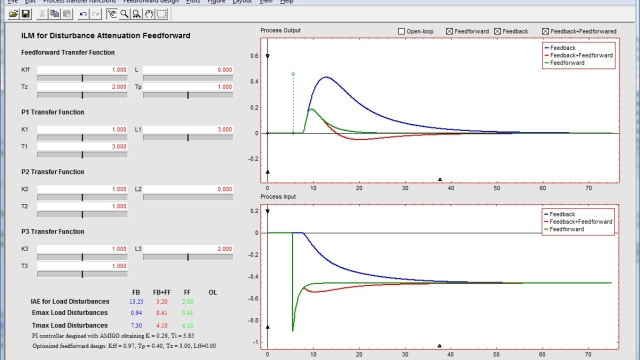
See MoreAn interactive feedforward tool for FeedForward Control
This interactive software tool is focused on basic and advanced concepts of feedforward control.
See More