Understanding PID Control, Part 7: Important PID Concepts
Now that you ’ve gotten an overview of PID tuning techniques, this video moves on to discussing two important concepts in PID control: cascaded loops and discrete systems. Both concepts are...
See MoreRobust Control, Part 2: Understanding Disk Margin
As we discussed in the last video, mathematical models aren’t a perfect representation of real systems. Therefore, we want to make sure that any system that is designed with those models is...
See MoreStanford Engineering Everywhere: CS223A - Introduction to Robotics
The purpose of this course is to introduce you to basics of modeling, design, planning, and control of robot systems. In essence, the material treated in this course is a brief survey of...
See MoreAn Introduction to the Kalman Filter
The purpose of this paper is to provide a practical introduction to the discrete Kalman filter. This introduction includes a description and some discussion of the basic discrete Kalman...
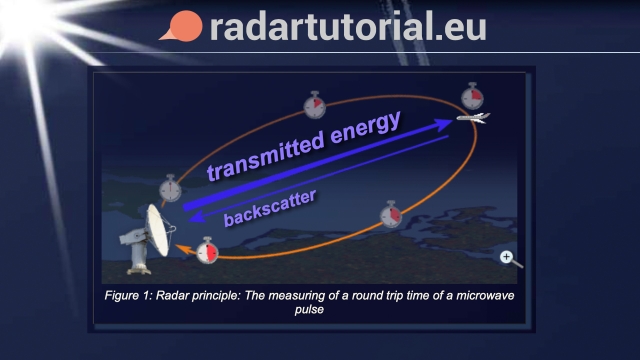
See MoreRadar Tutorial (English)
This page provides a detailed overview of radar principles and technologies, including mathematical, physical and technical explanations. “Radartutorial” explains the fundamentals of radar...
See MoreAn introduction to Beamforming
This video talks about how we actually have more control over the shape of the beam than just adding additional elements, or adjusting the position and orientation of the elements. We can...
See MoreUnderstanding Sensor Fusion and Tracking, Part 1: What Is Sensor Fusion?
This video provides an overview of what sensor fusion is and how it helps in the design of autonomous systems. It also covers a few scenarios that illustrate the various ways that sensor...
See MoreFree Video Course in Radar Systems Engineering
This Free Radar Systems Engineering Course (video, audio and screen captured ppt slides) and separate pdf slides) has been developed as a first course in Radar Systems for first year...
See MoreReinforcement Learning for Engineers, Part 4: The Walking Robot Problem
This video shows how to use the reinforcement learning workflow to get a bipedal robot to walk. It also looks at how to modify the default example to make it look more like how one would set...
See MoreAutonomous Navigation, Part 2: Understanding the Particle Filter
This video presents a high-level understanding of the particle filter and shows how it can be used in Monte Carlo localization to determine the pose of a mobile robot inside a building. We...
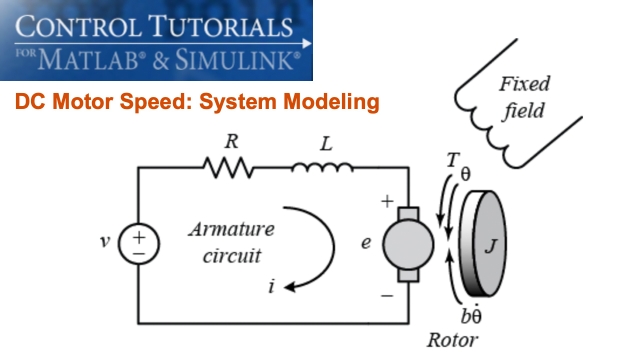
See MoreDC Motor Speed: System Modeling
This examples walks through modeling a simple DC motor in MATLAB.
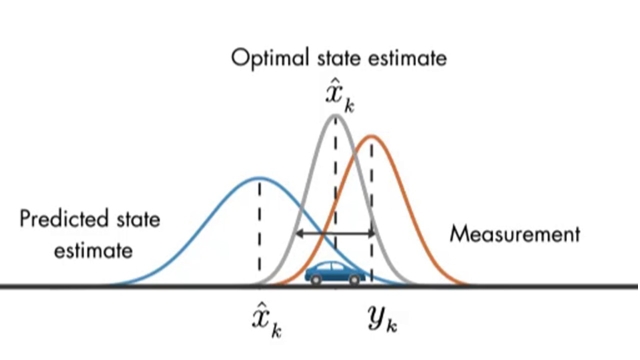
See MoreUnderstanding Kalman Filters, Part 3: An Optimal State Estimator
Watch this video for an explanation of how Kalman filters work. Kalman filters combine two sources of information, the predicted states and noisy measurements, to produce optimal, unbiased...
See MoreUnderstanding PID Control, Part 6: Manual and Automatic Tuning Methods
The previous video showed three different approaches to developing a mathematical model of your physical system. Now that we have this model, we can use it to tune a PID controller that will...
See MoreFMCW Radar for Autonomous Vehicles | Understanding Radar Principles
Watch an introduction to Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) radar and why it’s a good solution for autonomous vehicle applications. This demonstration will show how FMCW radar can...
See MoreUnderstanding Kalman Filters, Part 2: State Observers
Learn the working principles of state observers, and discover the math behind them. State observers are used for estimating the internal states of a system when you can’t directly measure...
See MoreAn Introduction to Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Learn what multi-agent reinforcement learning is and some of the challenges it faces and overcomes. You will also learn what an agent is and how multi-agent systems can be both cooperative...
See MoreWhat Are Dynamic Models? Chapter 1 from Dynamic Models in Biology
Throughout this book we use a wide-ranging set of case studies to illustrate different aspects of models and modeling. In this introductory chapter we describe and give examples of different...
See MoreSystem Identification Methods
System Identification is the process of determining the model or the equations of motion for your system. This is incredibly important because basing a control system design off of a bad...
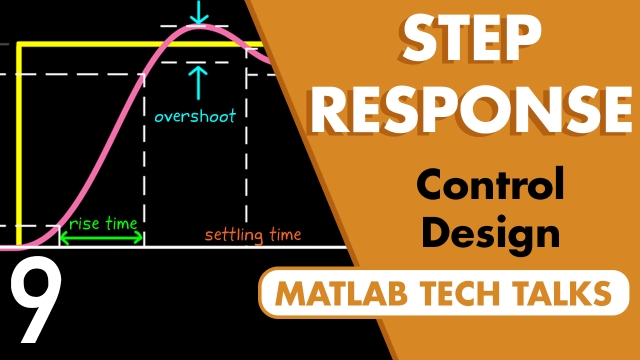
See MoreControl Systems in Practice, Part 9: The Step Response
This video covers a few interesting things about the step response. We’ll look at what a step response is and some of the ways it can be used to specify design requirements for closed loop...
See MoreUnderstanding PID Control, Part 4: A PID Tuning Guide
It can be difficult to navigate all the resources that promise to explain the secrets of PID tuning. Some proclaim that PID tuning is an art that requires finesse and experience, while...
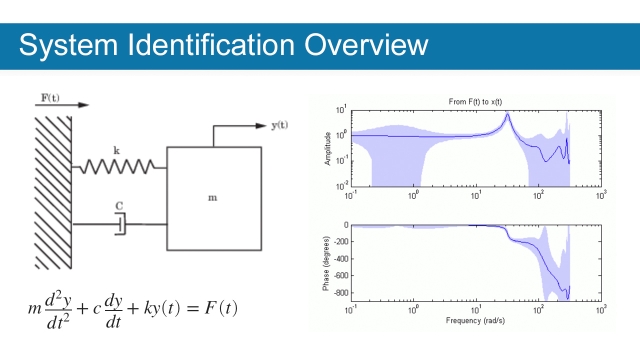
See MoreSystem Identification Overview
System identification is a methodology for building mathematical models of dynamic systems using measurements of the input and output signals of the system. This overview from Mathworks...
See MoreModeling Physical Systems, An Overview
This video sets the stage for the topics that I want to cover over the next month or two. This is an overview of how you go from a physical system to a linear model where you can design a...
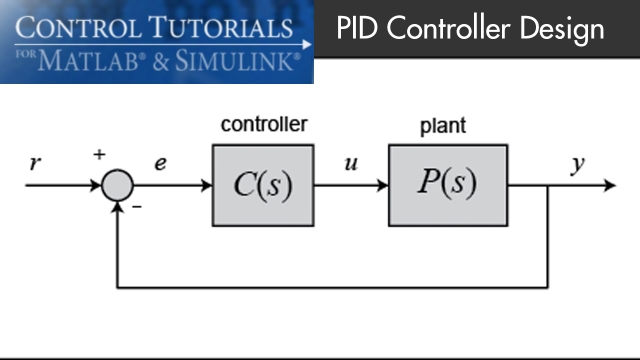
See MoreIntroduction: PID Controller Design
In this tutorial we will introduce a simple, yet versatile, feedback compensator structure: the Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller. The PID controller is widely employed...
See MoreAutonomous Navigation, Part 4: Path Planning with A* and RRT
This video explores some of the ways that we can use a map like a binary occupancy grid for motion and path planning. We briefly cover what motion planning means and how we can use a graph...
See MoreThe AVA Flight Computer
This video describes the board design, hardware architecture, and software components of the All Vehicle Avionics (AVA) flight computer that was designed by Joe Barnard of BPS Space. This...
See More