A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value, e(t), as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms (denoted P, I, and D respectively), hence the name.
Topic
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Controller
This topic includes the following resources and journeys:
Type
Experience
Scope
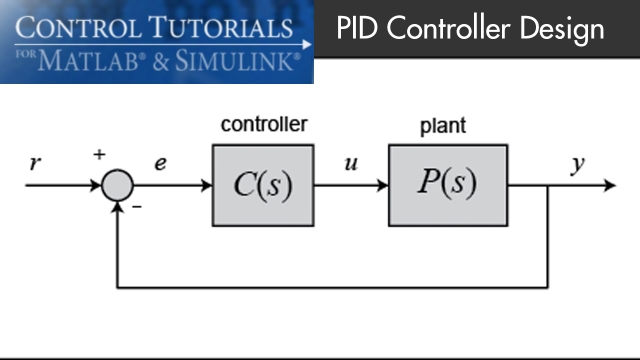
Introduction: PID Controller Design
In this tutorial we will introduce a simple, yet versatile, feedback compensator structure: the Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller. The PID controller is widely employed...
See MoreImproving the Beginner's PID - Introduction
In conjunction with the release of the new Arduino PID Library Brett has released this series of posts that explain his PID code. He start's with what he call's “The Beginner’s PID.” He...
See MoreTCLab PID Control
Implement a PID controller on the Temperature Control Lab hardware to drive the temperature from room temperature to 60 degrees C. This resource lets you attempt the design yourself first...
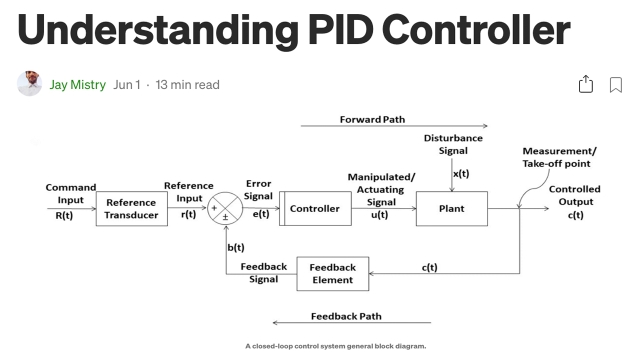
See MoreUnderstanding PID Controller
This blog post begins by walking through the basics and the theoretical part of the PID controllers. The controller is then tested, verified, and analyzed using MATLAB.
See More