A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value, e(t), as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms (denoted P, I, and D respectively), hence the name.
Topic
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Controller
This topic includes the following resources and journeys:
Filters
Type
Experience
Scope
54 items
Understanding PID Control, Part 3: Expanding Beyond a Simple Derivative
11 min
Beginner
Video
Theory
This video describes how to make an ideal PID controller more robust when controlling real systems that don’t behave like ideal linear models. Noise is generated by sensors and is present in...
See MoreUnderstanding PID Controller
13 min
Beginner
Article / Blog
Theory
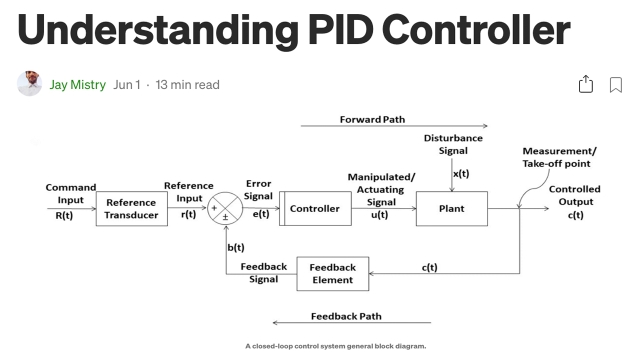
This blog post begins by walking through the basics and the theoretical part of the PID controllers. The controller is then tested, verified, and analyzed using MATLAB.
See MorePeter Ponders PID - Controlling an Under Damp Mass and Spring System
24 min
Beginner
Video
Theory
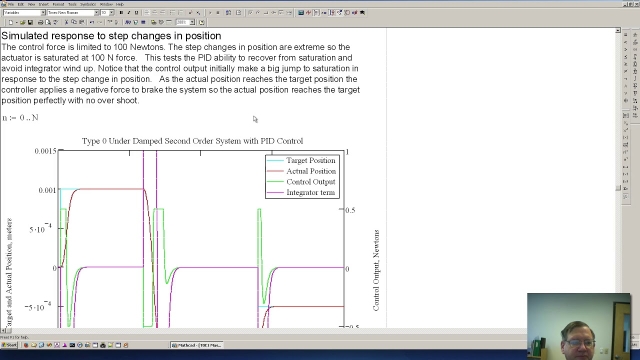
Demonstrates:How to calculate the PID gains. The importance of the derivative gain. How to simulate the mass and spring systemControl limitations based on s...
See MoreAn interactive feedforward tool for FeedForward Control
Beginner
App
Application
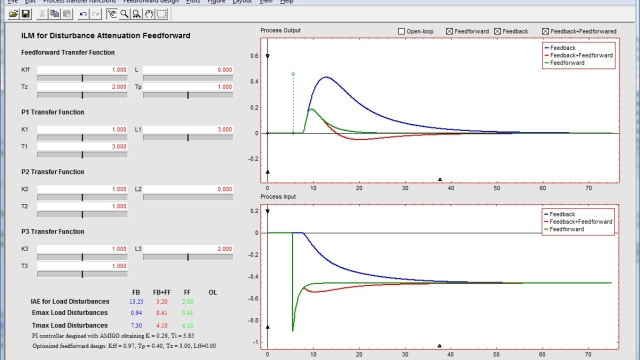
This interactive software tool is focused on basic and advanced concepts of feedforward control.
See More