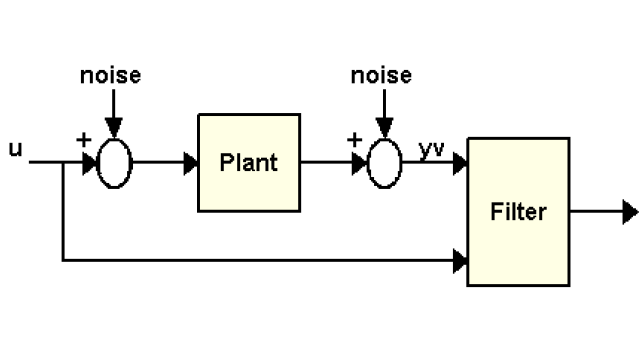
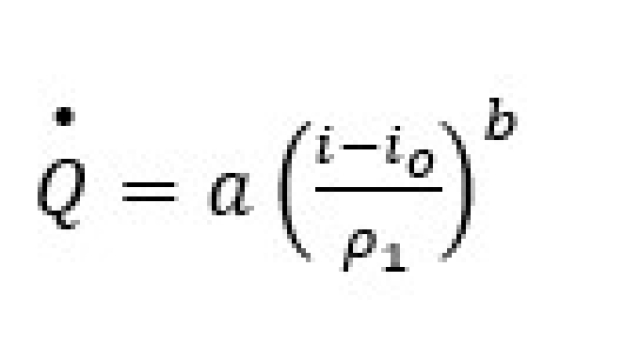Kalman Filter Design
This example shows how to perform Kalman filtering. Both a steady state filter and a time varying filter are designed and simulated.
See MoreIntroduction to Noise Filtering
Introduction to filtering - moving average, first-order, anti-aliasing, set point softening
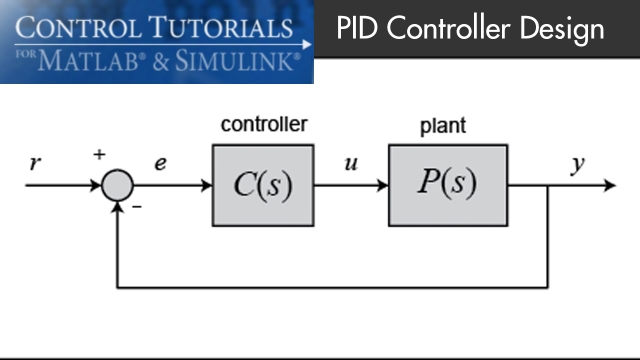
See MoreIntroduction: PID Controller Design
In this tutorial we will introduce a simple, yet versatile, feedback compensator structure: the Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller. The PID controller is widely employed...
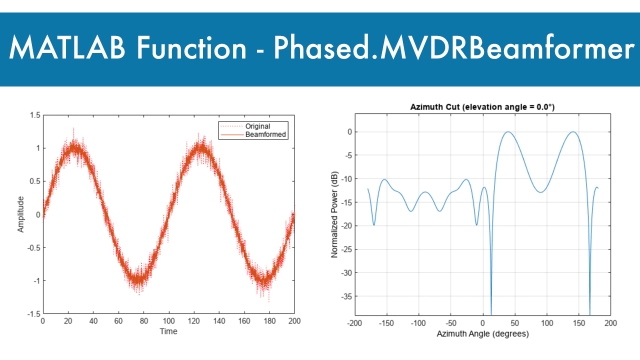
See MoreMATLAB Function: phased.MVDRBeamformer
The phased.MVDRBeamformer System object™ implements a narrowband minimum-variance distortionless-response (MVDR) beamformer. The MVDR beamformer is also called the Capon beamformer. An MVDR...
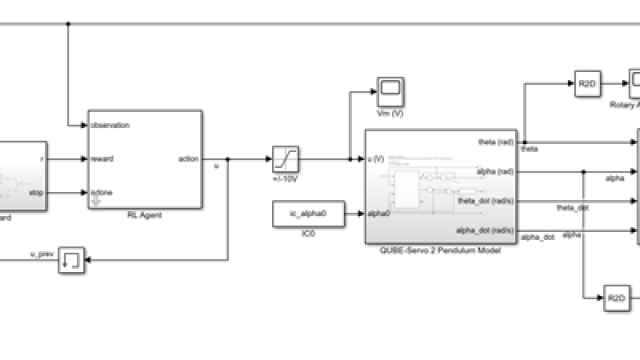
See MoreUsing the Reinforcement Learning Toolbox™ to Balance an Inverted Pendulum
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a subset of Machine Learning that uses dynamic data, not static data like unsupervised learning or supervised learning. Reinforcement learning is used in many...
See MoreTCLab PID Control
Implement a PID controller on the Temperature Control Lab hardware to drive the temperature from room temperature to 60 degrees C. This resource lets you attempt the design yourself first...
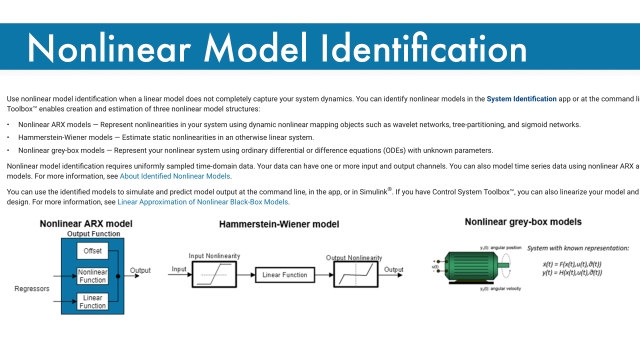
See MoreNonlinear Model Identification
Mathwork overview page describing nonlinear model identification. Use nonlinear model identification when a linear model does not completely capture your system dynamics. You can identify...
See MoreImproving the Beginner's PID - Introduction
In conjunction with the release of the new Arduino PID Library Brett has released this series of posts that explain his PID code. He start's with what he call's “The Beginner’s PID.” He...
See MoreRoad Sign Detection using Transfer Learning on RetinaNet
This blog outlines a number of open-source resources for transfer learning that are worthy of exploring, ands show the result of using transfer learning on RetinaNet to develop a road sign...
See MoreControl Valve Problems
Control valve problems can severely affect control loop performance and, unless eliminated, they can make controller tuning a challenging (sometimes impossible) task. Some problems are quite...
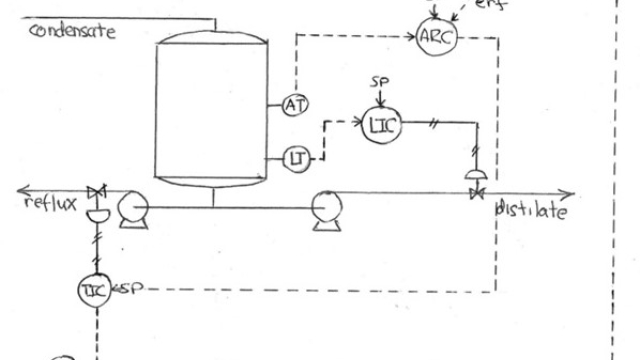
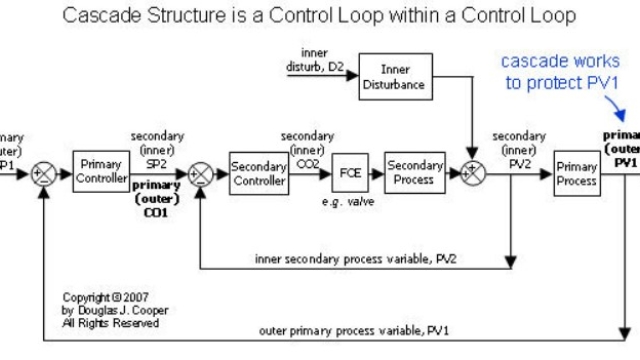
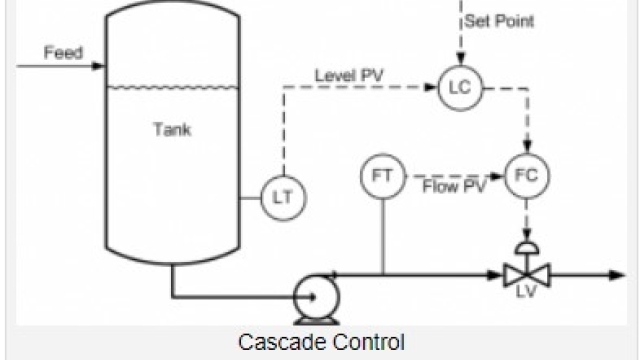
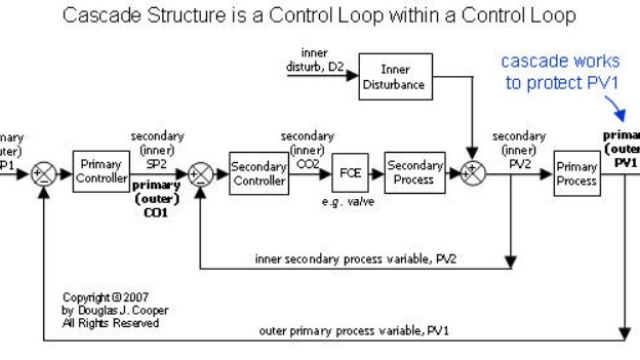
See MoreCascade Control
When and how to use Cascade Control
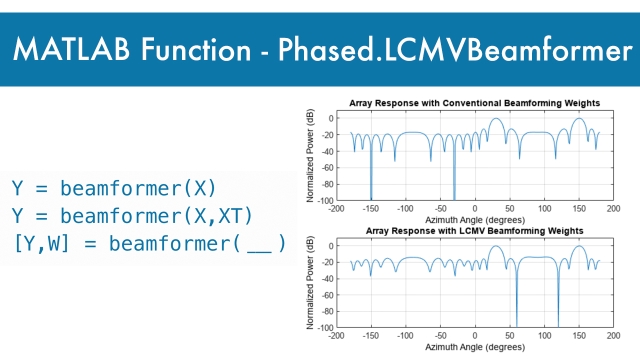
See MoreMATLAB function: phased.LCMVBeamformer
The phased.LCMVBeamformer object implements a narrowband linear-constraint minimum-variance (LCMV) beamformer for a sensor array. The LCMV beamformer belongs to the family of constrained...
See MoreBumpless Transfer and Tuning
Switching from MAN to AUTO mode or LOCAL to CASCADE or changing the controller integral time should not cause a change in the controller output, a bump. But a primitive coding of the PID...
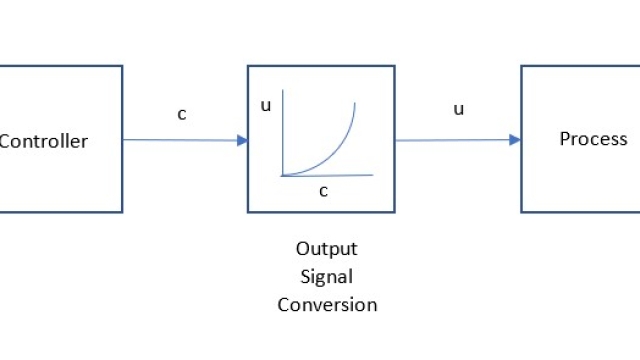
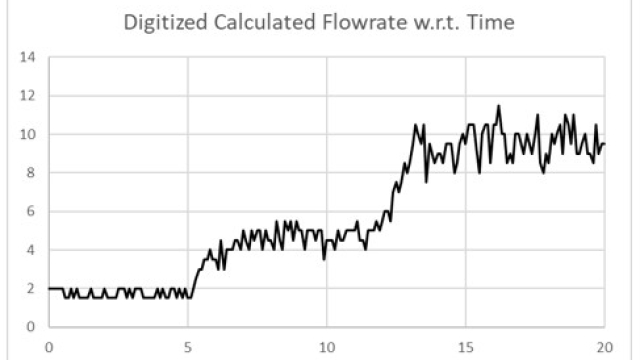
See MoreNonlinear Control Output Signal Characterization
If the process gain makes large changes over the operating range, then tuning PID (or other linear) controllers is difficult. If tuned for one region, the controller is undesirably sluggish...
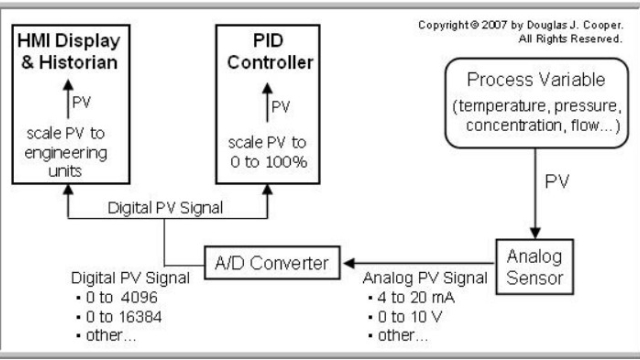
See MoreMeasurements, Transmission Signals, and Issues
This is an introduction to scaled information transmission signals (for example 4-20 mA, 3-15 psig, etc.), the actual sensed signals (like using orifice dP to infer flow rate, or temperature...
See MoreCascade Control 2
An Implementation Recipe for Cascade Control
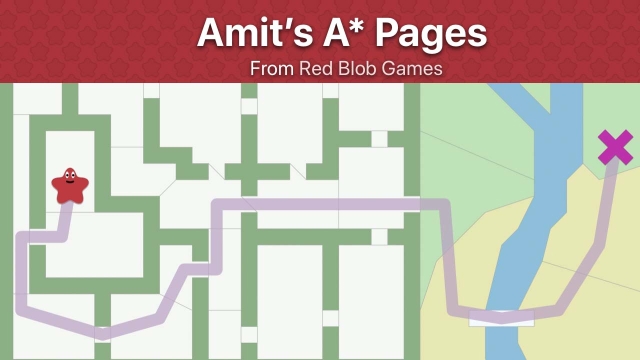
See MoreIntroduction to the A* Algorithm
An interactive visual explanation of the A* algorithm using motivating examples from computer games.
See More
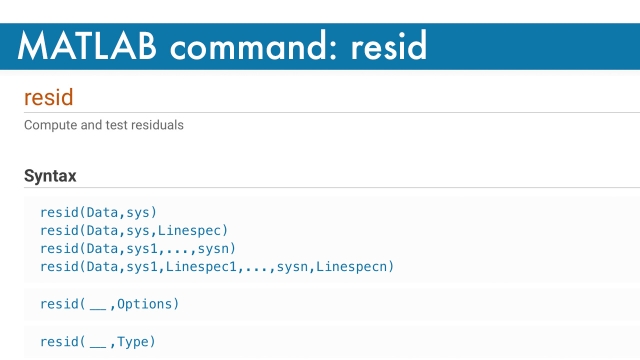
MATLAB Command: resid
This MATLAB command is part of the system identification toolbox and provides a way to compute and test residuals.
See MoreCascade Control
What is Cascade Control and why use it?
See MoreScaled Transmission Signals, Engineering Units, and Conversions
Information is transmitted in scaled signals (4-20 mA, 3-15 psig, 0-100%, digital counts), which are also deviations from some reference vales (such as psi gage is to psia). But process...
See MoreMATLAB Command: lqr
MATLAB command documentation for the Linear-Quadratic Regulator (lqr) function.
See MoreOrifice Calibration
The ISO method for orifice design and calibration is grounded in the ideal square-root relation between pressure drop and flow rate, specifies the in-pipe structure for an orifice, and...
See MorePathfinding with A*
An interactive visual explanation of the A* pathfinding algorithm. This resource uses motivating examples from computer games.
See More
Linear Model Identification Basics
This is a curated list of Mathworks products, examples, and topics that cover identifying linear models, selecting suitable model structures, constructing and modifying model object...
See More