A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value, e(t), as the difference between a desired setpoint (SP) and a measured process variable (PV) and applies a correction based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms (denoted P, I, and D respectively), hence the name.
Topic
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) Controller
This topic includes the following resources and journeys:
Type
Experience
Scope
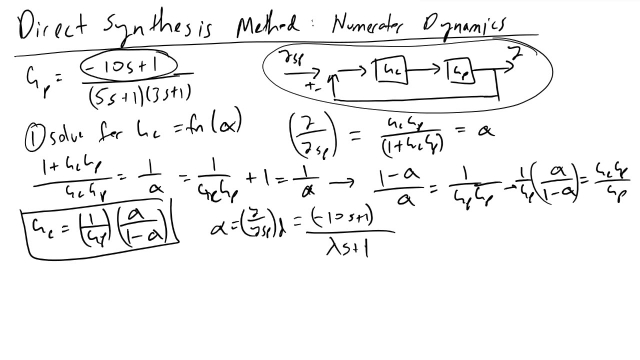
Direct Synthesis Method Numerator Dynamics Problem
I walk through how to design a PID feedback controller when given a second order process with numerator dynamics, using the Direct Synthesis Method.
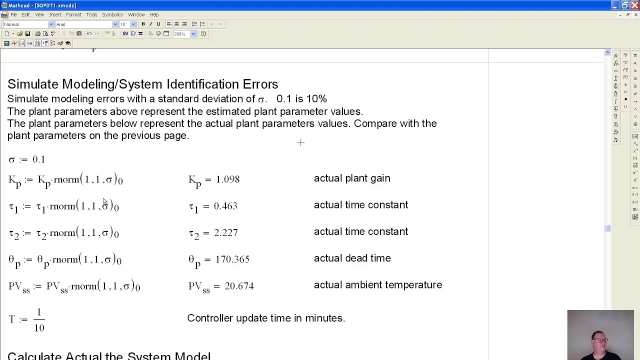
See MorePeter Ponders PID. Second Order Plus Dead Time , SOPDT, Temperature Control,...
In this video I derive the equations for the controller gains and a low pass filter for a SOPDT system with a very long dead time To make the simulation mo...
See MoreUnderstanding PID Control, Part 2: Expanding Beyond a Simple Integral
The first video in this series described a PID controller, and it showed how each of the three branches help control your system.That seemed simple enough and appeared to work. However, in...
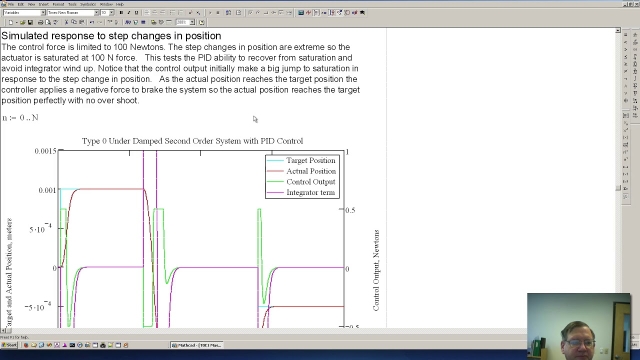
See MorePeter Ponders PID - Controlling an Under Damp Mass and Spring System
Demonstrates:How to calculate the PID gains. The importance of the derivative gain. How to simulate the mass and spring systemControl limitations based on s...
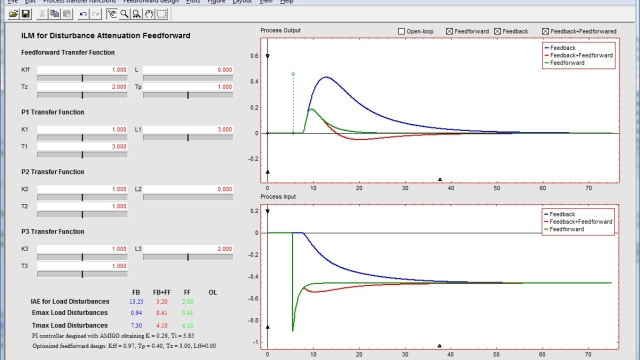
See MoreAn interactive feedforward tool for FeedForward Control
This interactive software tool is focused on basic and advanced concepts of feedforward control.
See More