The theory of belief functions, also referred to as evidence theory or Dempster–Shafer theory (DST), is a general framework for reasoning with uncertainty, with understood connections to other frameworks such as probability, possibility and imprecise probability theories. First introduced by Arthur P. Dempster in the context of statistical inference, the theory was later developed by Glenn Shafer into a general framework for modeling epistemic uncertainty—a mathematical theory of evidence. The theory allows one to combine evidence from different sources and arrive at a degree of belief (represented by a mathematical object called belief function) that takes into account all the available evidence.
Topic
Evidence Theory
This topic includes the following resources and journeys:
Filters
Type
Experience
Scope
3 items
Overview of Dempster-Shafer Theory (Evidence Theory)
Beginner
Article / Blog
Theory
This is an overview of Dempster-Shafer Theory (Evidence Theory) that provides an introduction, definition, basic information about combination rules, some issues with the theory, and the...
See MoreAutomatic Updates of Transition Potential Matrices in Dempster-Shafer Networ...
Advanced
Peer Reviewed Paper
Theory
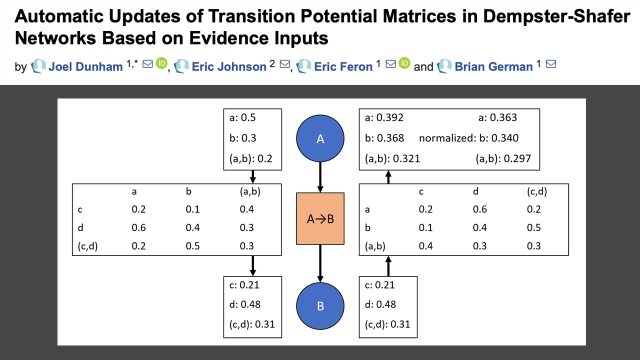
Journal article that develops an evidential reasoning network capable of learning/updating the relationships between Frames of Discernment (the sets over which Dempster-Shafer reasons that...
See MoreSmart Projectile State Estimation Using Evidence Theory
Intermediate
Peer Reviewed Paper
Theory
This journal article provides a very good practical understanding of Dempster-Shafer theory using sensor fusion and state estimation as the backdrop.
See More