A digital twin is a digital replica of a living or non-living physical entity. Digital twin refers to a digital replica of potential and actual physical assets (physical twin), processes, people, places, systems and devices that can be used for various purposes. The digital representation provides both the elements and the dynamics of how an Internet of things (IoT) device operates and lives throughout its life cycle. Definitions of digital twin technology used in prior research emphasize two important characteristics. Firstly, each definition emphasizes the connection between the physical model and the corresponding virtual model or virtual counterpart. Secondly, this connection is established by generating real-time data using sensors. The concept of the digital twin can be compared to other concepts such as cross-reality environments or co-spaces and mirror models, which aim to, by and large, synchronize part of the physical world (e.g., an object or place) with its cyber representation (which can be an abstraction of some aspects of the physical world).
Topic
Digital Twin
This topic includes the following resources and journeys:
Type
Experience
Scope
Post-Pandemic: A Hybrid Lab Experience
This article discusses the importance of a hybrid laboratory model, blending physical hardware with digital twins. Example using the Quanser Interactive Lab (QLabs) platform is given.
See MoreA Hybrid Lab Experience: Blending Hands-on Explorations with the Flexibility...
This case study examines how the Earth and Space Science and Engineering (ESSE) department at York University in Toronto offered a meaningful remote laboratory experience to over 180...
See MoreDigital Twin Parameter Tuning
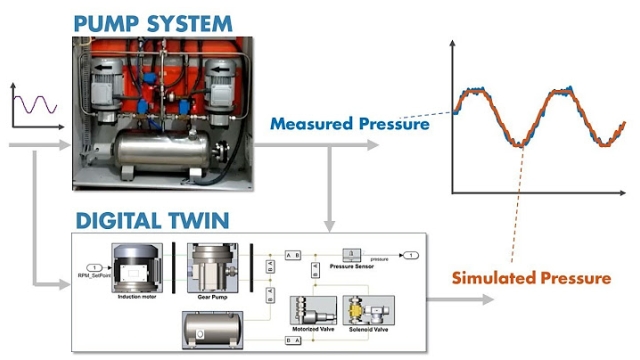
Learn how to tune the digital twin model of a pump system to its physical asset using Simulink Design Optimization™. You can use measured data collected from the physical system to tune the...
See MoreDigital Twins
This lecture discusses the use of data-driven digital twins in advanced model-based design and engineering, and the related digital thread, which ties together the data throughout an entire...
See More